This geom is a cousin of ggplot2::geom_polygon() with the added
possibility of expanding or contracting the polygon by an absolute amount
(e.g. 1 cm). Furthermore, it is possible to round the corners of the polygon,
again by an absolute amount. The resulting geom reacts to resizing of the
plot, so the expansion/contraction and corner radius will not get distorted.
If no expansion/contraction or corner radius is specified, the geom falls
back to geom_polygon so there is no performance penality in using this
instead of geom_polygon.
Usage
geom_shape(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "identity",
position = "identity",
expand = 0,
radius = 0,
...,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes(). If specified andinherit.aes = TRUE(the default), it is combined with the default mapping at the top level of the plot. You must supplymappingif there is no plot mapping.- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options:
If
NULL, the default, the data is inherited from the plot data as specified in the call toggplot().A
data.frame, or other object, will override the plot data. All objects will be fortified to produce a data frame. Seefortify()for which variables will be created.A
functionwill be called with a single argument, the plot data. The return value must be adata.frame, and will be used as the layer data. Afunctioncan be created from aformula(e.g.~ head(.x, 10)).- stat
The statistical transformation to use on the data for this layer. When using a
geom_*()function to construct a layer, thestatargument can be used the override the default coupling between geoms and stats. Thestatargument accepts the following:A
Statggproto subclass, for exampleStatCount.A string naming the stat. To give the stat as a string, strip the function name of the
stat_prefix. For example, to usestat_count(), give the stat as"count".For more information and other ways to specify the stat, see the layer stat documentation.
- position
A position adjustment to use on the data for this layer. This can be used in various ways, including to prevent overplotting and improving the display. The
positionargument accepts the following:The result of calling a position function, such as
position_jitter(). This method allows for passing extra arguments to the position.A string naming the position adjustment. To give the position as a string, strip the function name of the
position_prefix. For example, to useposition_jitter(), give the position as"jitter".For more information and other ways to specify the position, see the layer position documentation.
- expand
A numeric or unit vector of length one, specifying the expansion amount. Negative values will result in contraction instead. If the value is given as a numeric it will be understood as a proportion of the plot area width.
- radius
As
expandbut specifying the corner radius.- ...
Other arguments passed on to
layer()'sparamsargument. These arguments broadly fall into one of 4 categories below. Notably, further arguments to thepositionargument, or aesthetics that are required can not be passed through.... Unknown arguments that are not part of the 4 categories below are ignored.Static aesthetics that are not mapped to a scale, but are at a fixed value and apply to the layer as a whole. For example,
colour = "red"orlinewidth = 3. The geom's documentation has an Aesthetics section that lists the available options. The 'required' aesthetics cannot be passed on to theparams. Please note that while passing unmapped aesthetics as vectors is technically possible, the order and required length is not guaranteed to be parallel to the input data.When constructing a layer using a
stat_*()function, the...argument can be used to pass on parameters to thegeompart of the layer. An example of this isstat_density(geom = "area", outline.type = "both"). The geom's documentation lists which parameters it can accept.Inversely, when constructing a layer using a
geom_*()function, the...argument can be used to pass on parameters to thestatpart of the layer. An example of this isgeom_area(stat = "density", adjust = 0.5). The stat's documentation lists which parameters it can accept.The
key_glyphargument oflayer()may also be passed on through.... This can be one of the functions described as key glyphs, to change the display of the layer in the legend.
- na.rm
If
FALSE, the default, missing values are removed with a warning. IfTRUE, missing values are silently removed.- show.legend
logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
NA, the default, includes if any aesthetics are mapped.FALSEnever includes, andTRUEalways includes. It can also be a named logical vector to finely select the aesthetics to display.- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics, rather than combining with them. This is most useful for helper functions that define both data and aesthetics and shouldn't inherit behaviour from the default plot specification, e.g.borders().
Note
Some settings can result in the dissappearance of polygons, specifically when contracting or rounding corners with a relatively large amount. Also note that x and y scale limits does not take expansion into account and the resulting polygon might thus not fit into the plot.
Aesthetics
geom_shape understand the following aesthetics (required aesthetics are in bold):
x
y
color
fill
group
size
linetype
alpha
Examples
shape <- data.frame(
x = c(0.5, 1, 0.75, 0.25, 0),
y = c(0, 0.5, 1, 0.75, 0.25)
)
# Expand and round
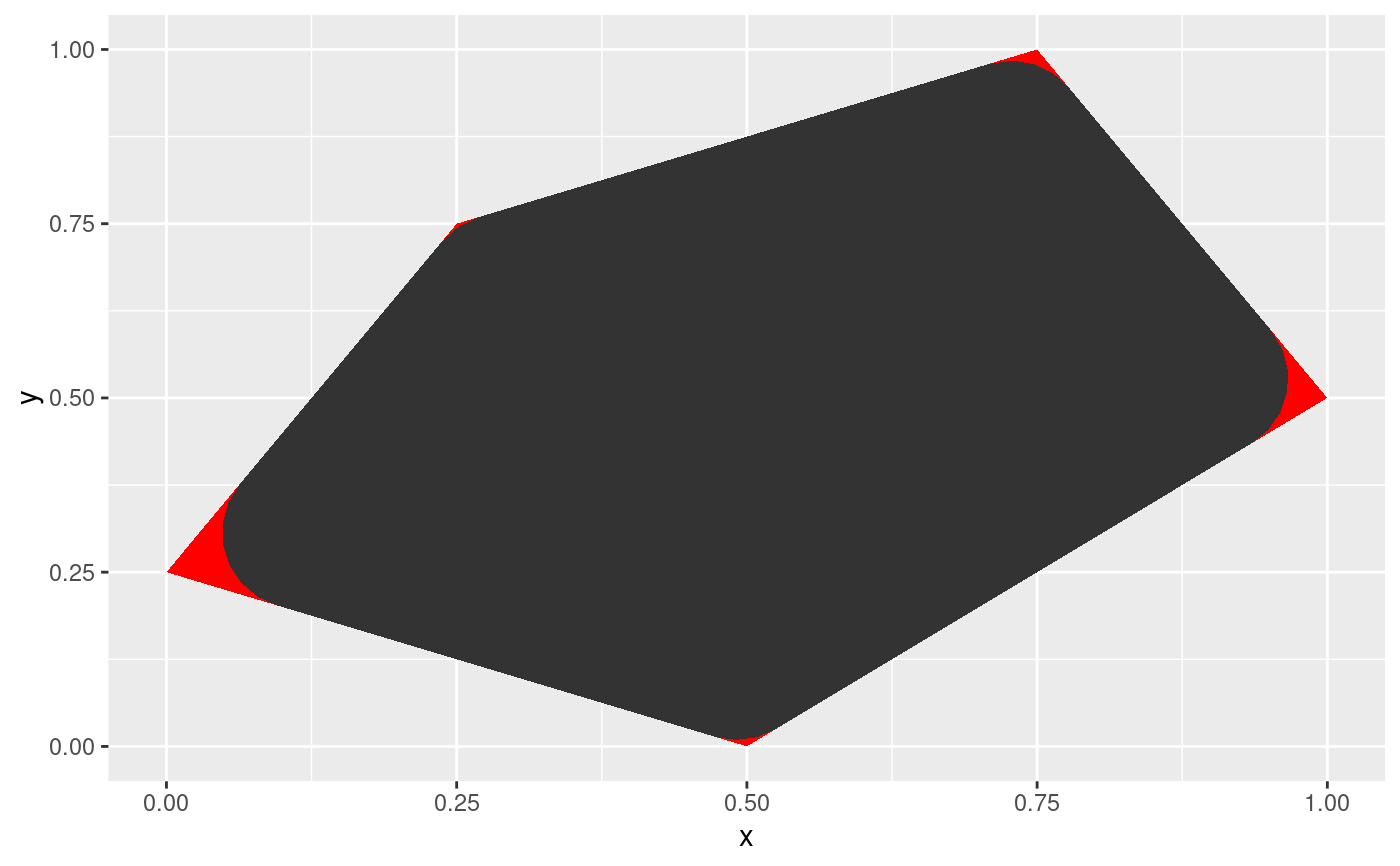
ggplot(shape, aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_shape(expand = unit(1, 'cm'), radius = unit(0.5, 'cm')) +
geom_polygon(fill = 'red')
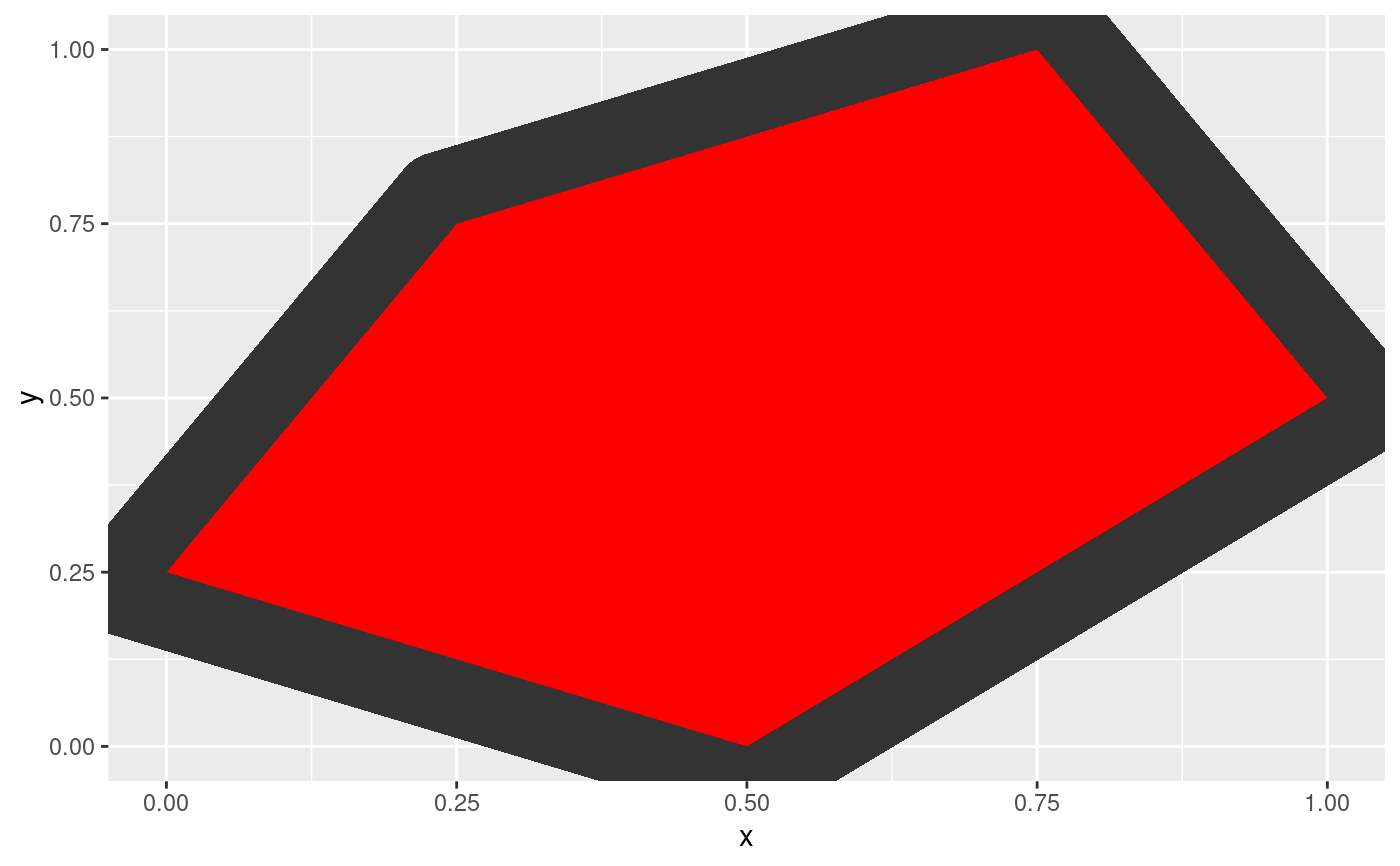 # Contract
ggplot(shape, aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_polygon(fill = 'red') +
geom_shape(expand = unit(-1, 'cm'))
# Contract
ggplot(shape, aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_polygon(fill = 'red') +
geom_shape(expand = unit(-1, 'cm'))
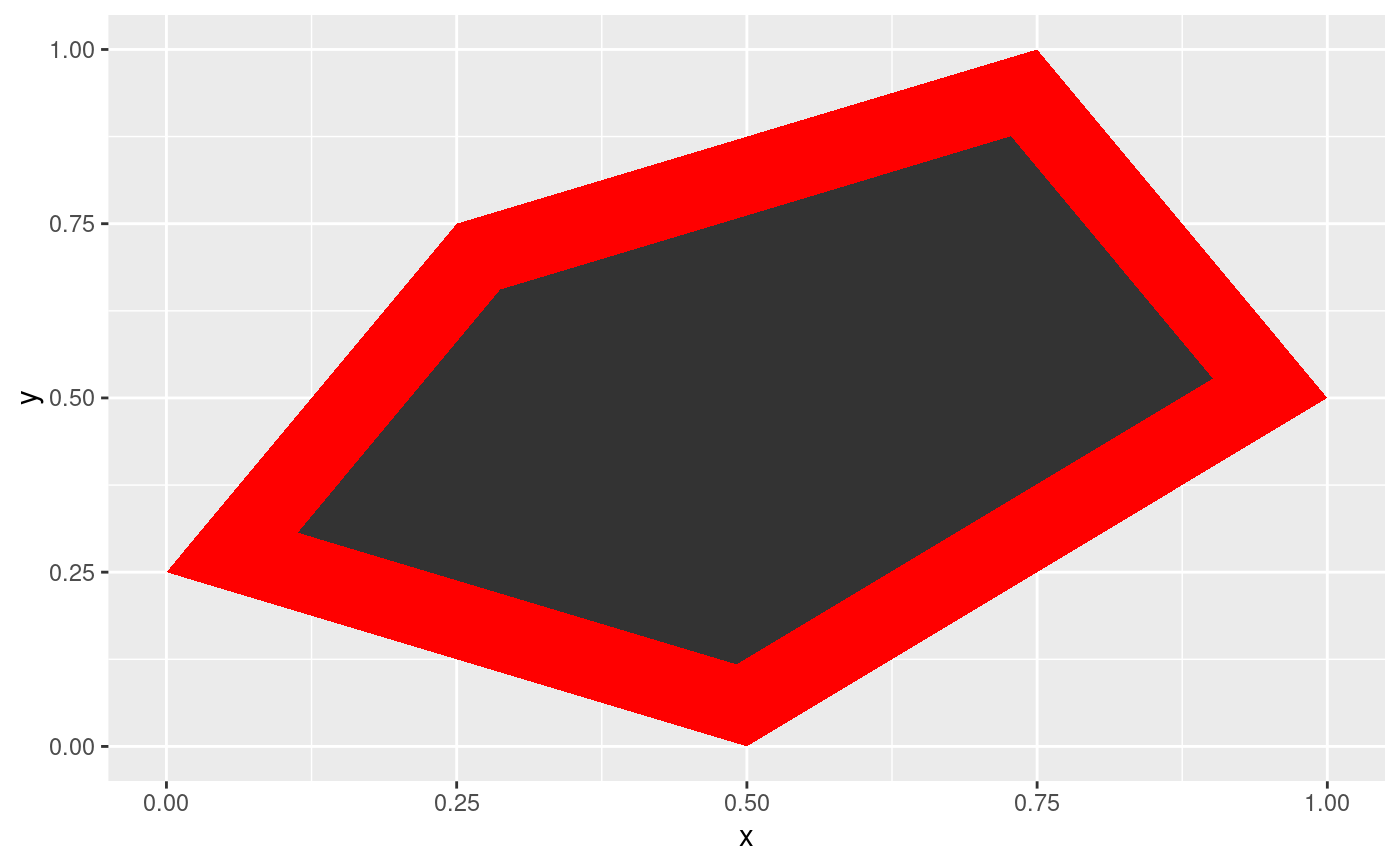 # Only round corners
ggplot(shape, aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_polygon(fill = 'red') +
geom_shape(radius = unit(1, 'cm'))
# Only round corners
ggplot(shape, aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_polygon(fill = 'red') +
geom_shape(radius = unit(1, 'cm'))