This position adjustment is able to select a meaningful jitter of the data based on the combination of positional scale types. It behaves differently depending on if none, one, or both the x and y scales are discrete. If both are discrete it will jitter the datapoints evenly inside a disc, if one of them is discrete it will jitter the discrete dimension to follow the density along the other dimension (like a sina plot). If neither are discrete it will not do any jittering.
Arguments
- jitter.width
The maximal width of the jitter
- bw
The smoothing bandwidth to use in the case of sina jittering. See the
bwargument in stats::density- scale
Should the width of jittering be scaled based on the number of points in the group
- seed
A seed to supply to make the jittering reproducible across layers
See also
geom_autopoint for a point geom that uses auto-position by default
Examples
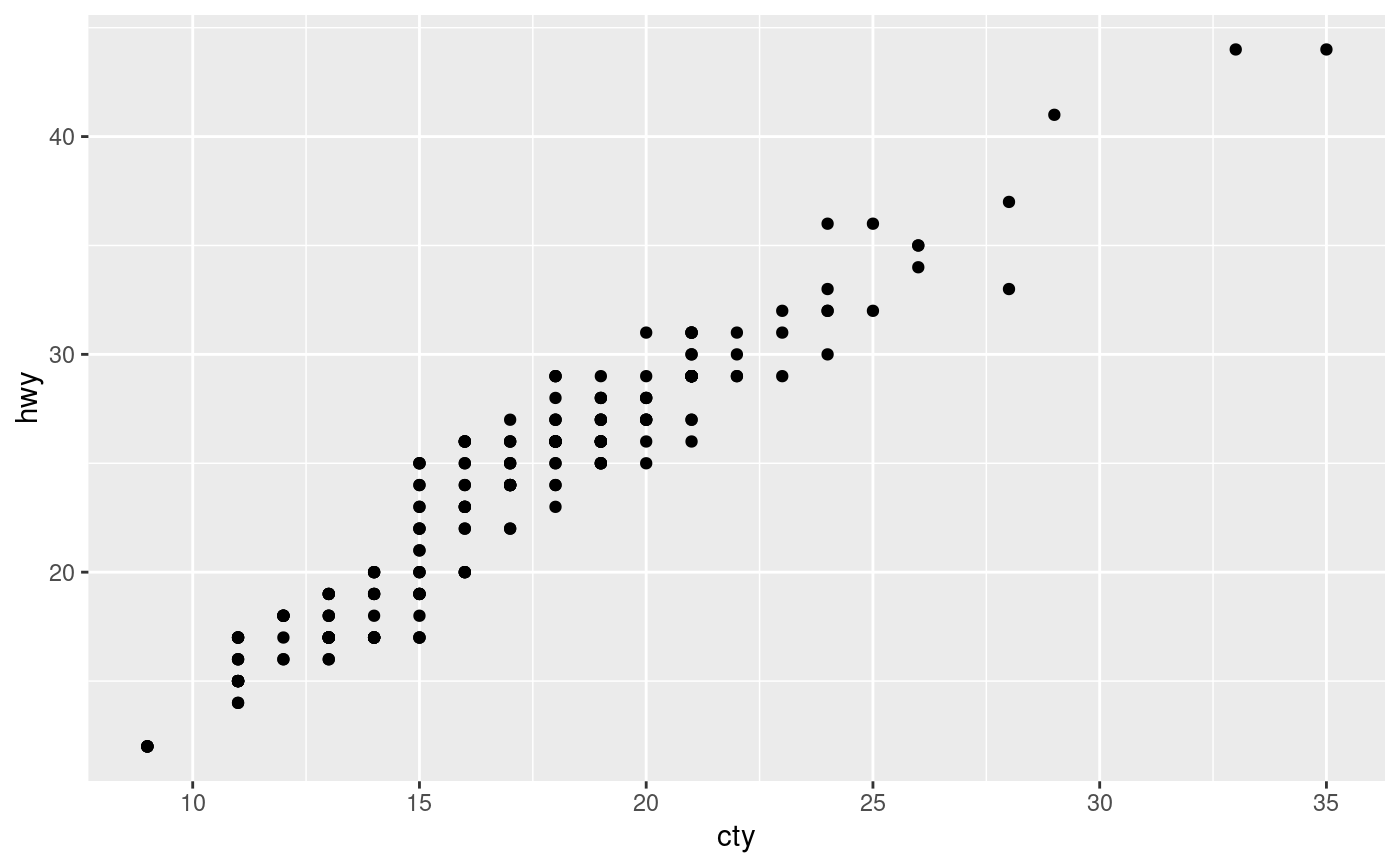
# Continuous vs continuous: No jitter
ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(cty, hwy), position = 'auto')
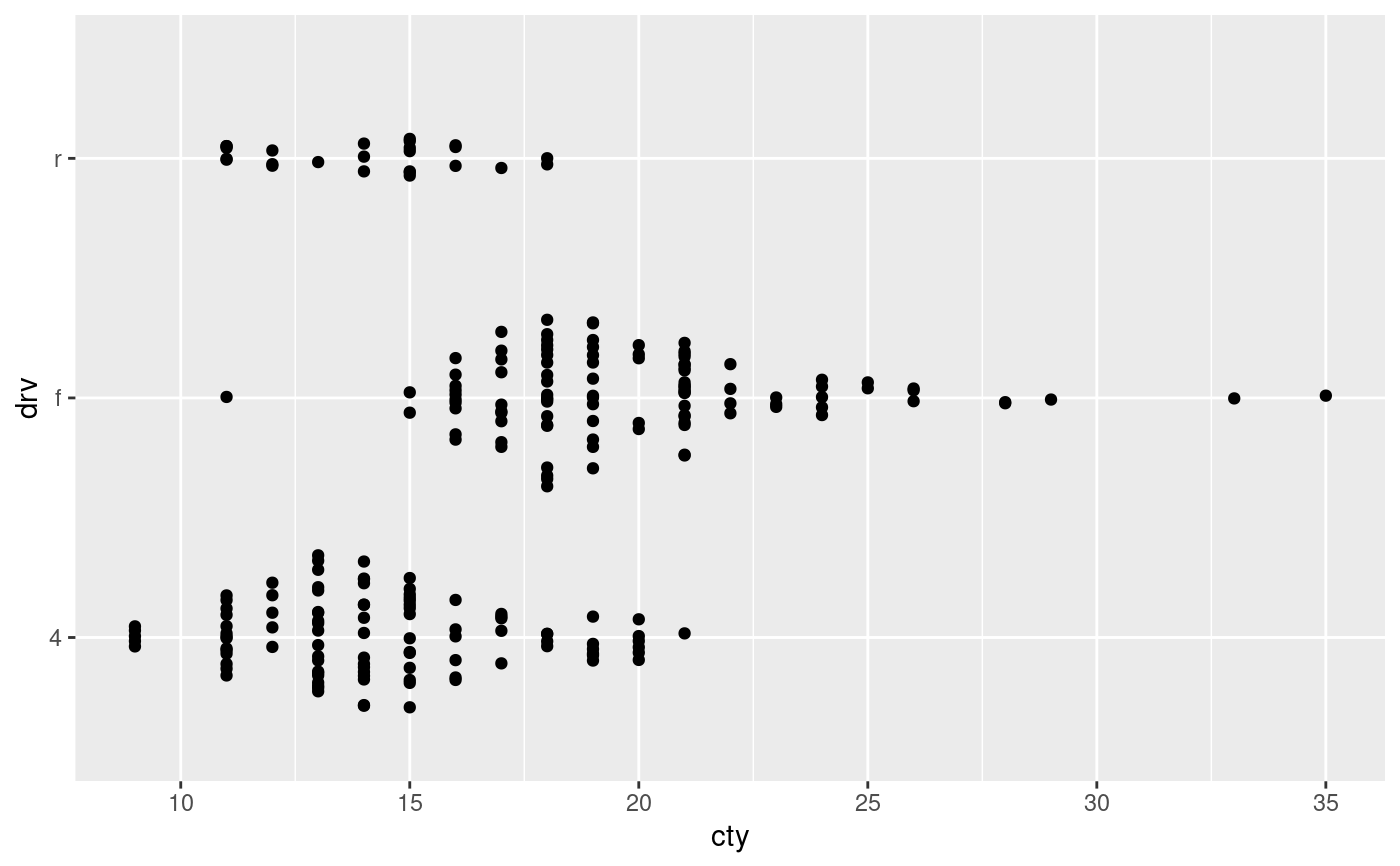
 # Continuous vs discrete: sina jitter
ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(cty, drv), position = 'auto')
# Continuous vs discrete: sina jitter
ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(cty, drv), position = 'auto')
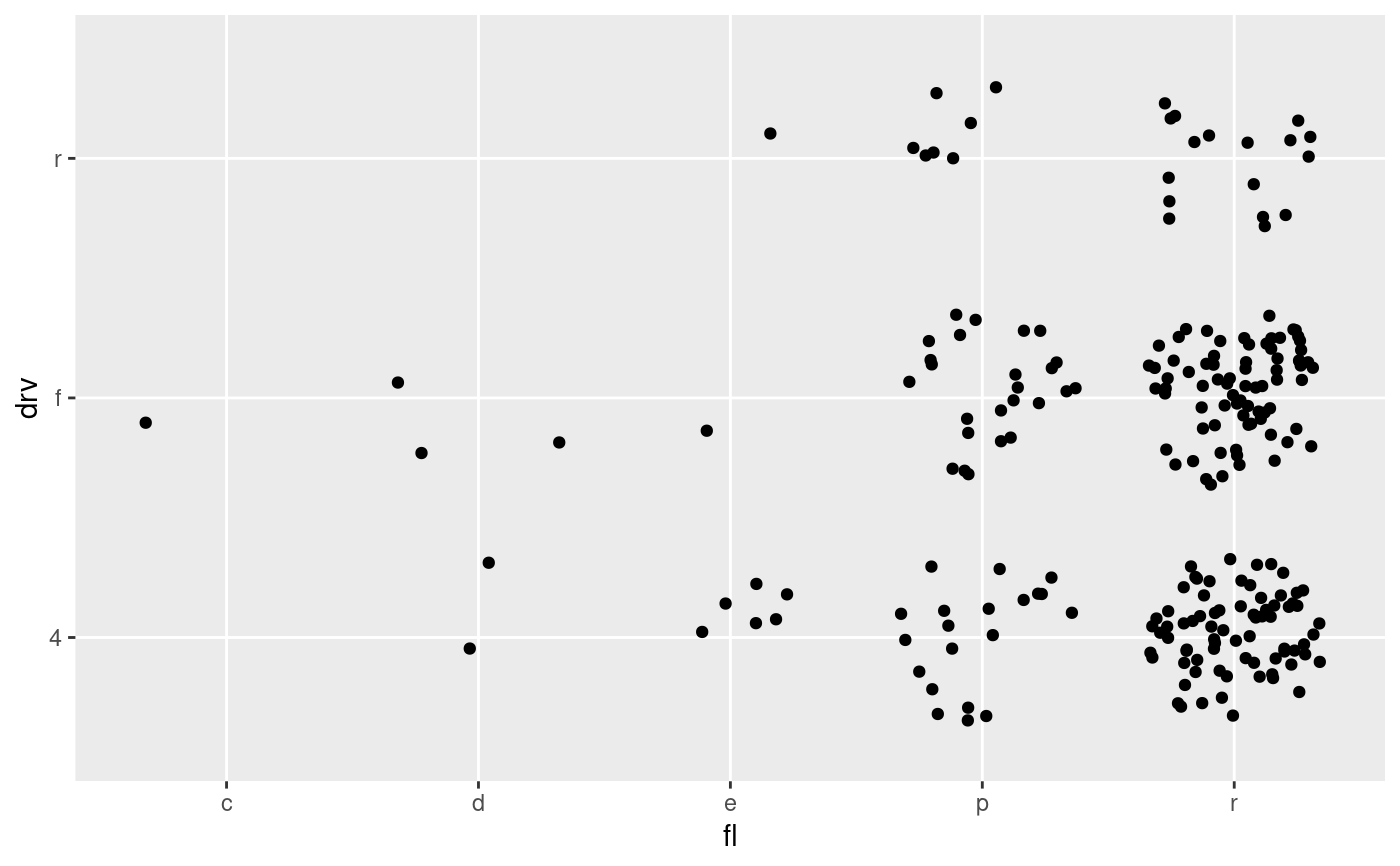
 # Discrete vs discrete: disc-jitter
ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(fl, drv), position = 'auto')
# Discrete vs discrete: disc-jitter
ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(fl, drv), position = 'auto')
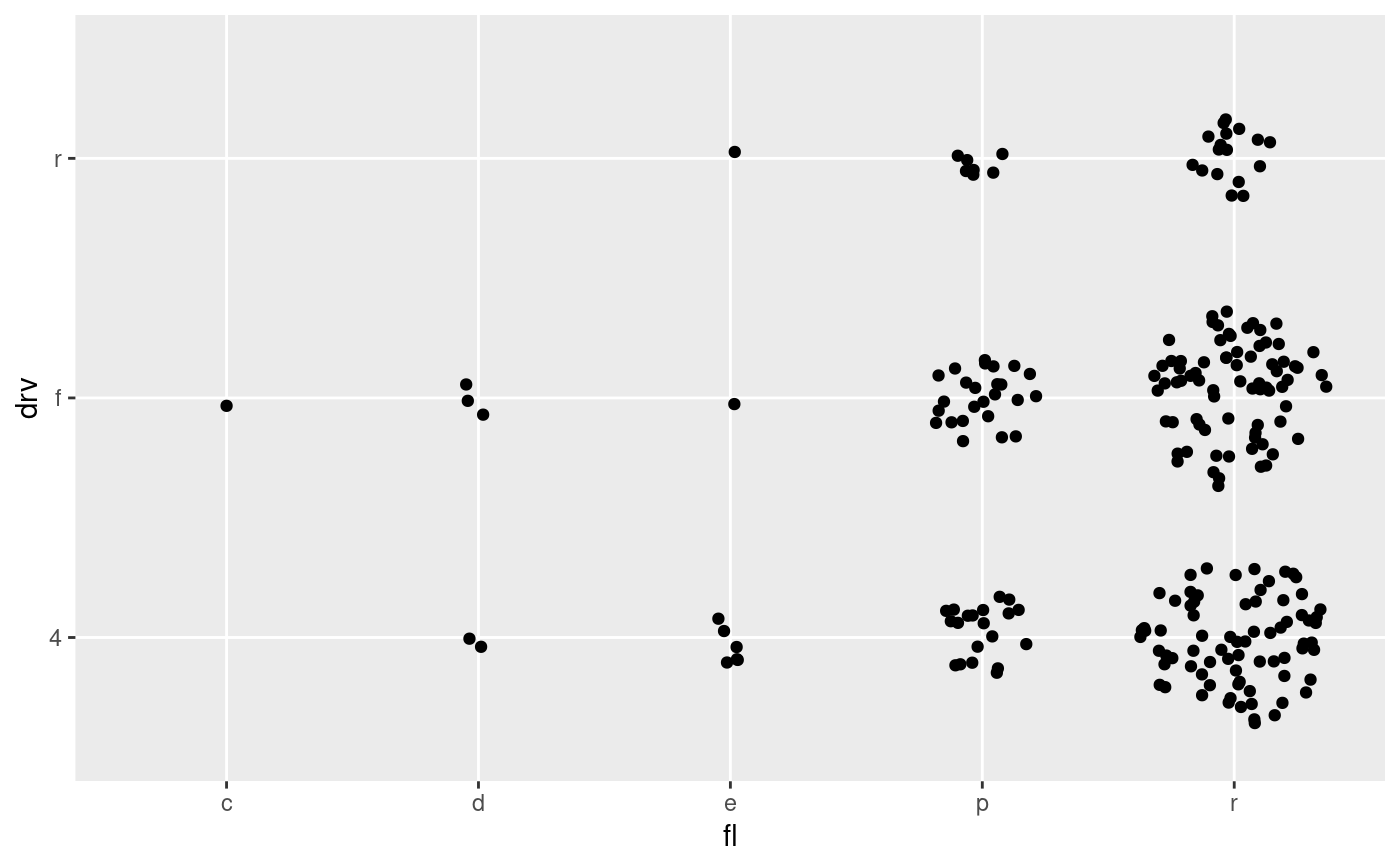 # Don't scale the jitter based on group size
ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(cty, drv), position = position_auto(scale = FALSE))
# Don't scale the jitter based on group size
ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(cty, drv), position = position_auto(scale = FALSE))
 ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(fl, drv), position = position_auto(scale = FALSE))
ggplot(mpg) + geom_point(aes(fl, drv), position = position_auto(scale = FALSE))